

Why Clients Choose Silver Runner: Our Geography and Key Advantage
We share our key operational areas and the unique product that saves our clients’ budgets.




It is one of the key factors that determine the compatibility and interoperability of trains and tracks across different countries and regions.
In Europe, there are several track gauges in use, ranging from 600 mm (1 ft 11 5⁄8 in) to 1,668 mm (5 ft 5 21⁄32 in). However, the most common and widely used track gauge is the standard gauge, which measures 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in).


The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it.
In Europe, the standard gauge covers most of the high-speed rail networks and many conventional rail lines. It is also compatible with the European Train Control System (ETCS), which is the signalling and control component of the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS).


The ETCS is designed to replace the many incompatible safety systems currently used by European railways. It aims to achieve interoperability and harmonisation of train operations across Europe, as well as to increase safety, reliability and efficiency of rail transport. The ETCS consists of standard trackside equipment and unified controlling equipment within the train cab. It allows for continuous or intermittent exchange of information between track and trains, depending on the level of application. The ETCS also enables wireless transmission of all lineside information to the driver inside the cab, removing the need for lineside signals.
The adoption of the standard gauge and the ETCS in Europe has been driven by several factors, such as the economic integration of the European Union (EU), the liberalisation of national railway markets, and the development of high-speed rail projects. The EU has issued directives on the interoperability of high-speed and conventional rail systems, requiring all new, upgraded or renewed tracks and rolling stock to adopt ETCS. However, the deployment of ETCS has been slow and uneven across Europe, due to technical challenges, high costs, lack of business case and resistance from some national operators.
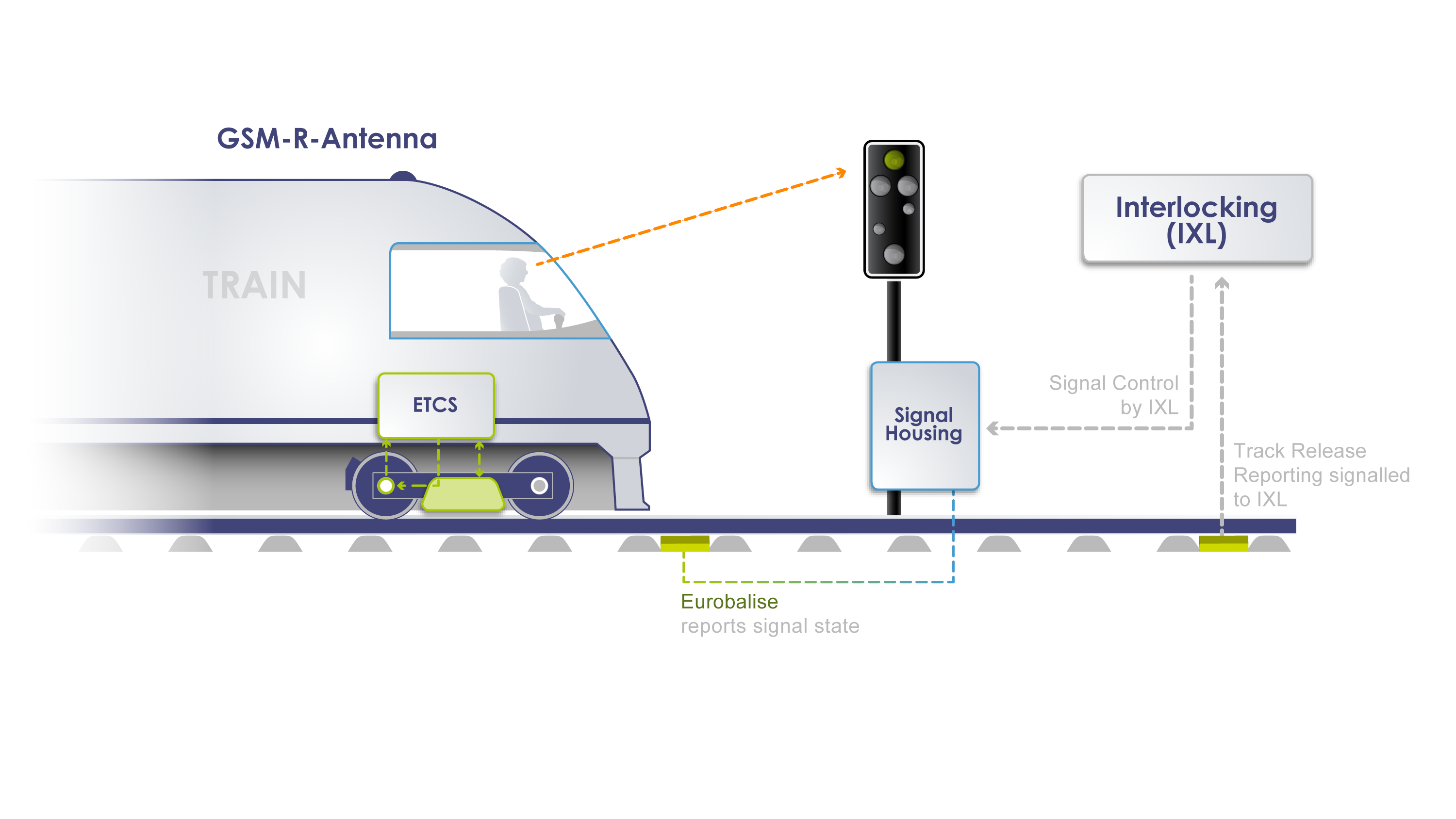

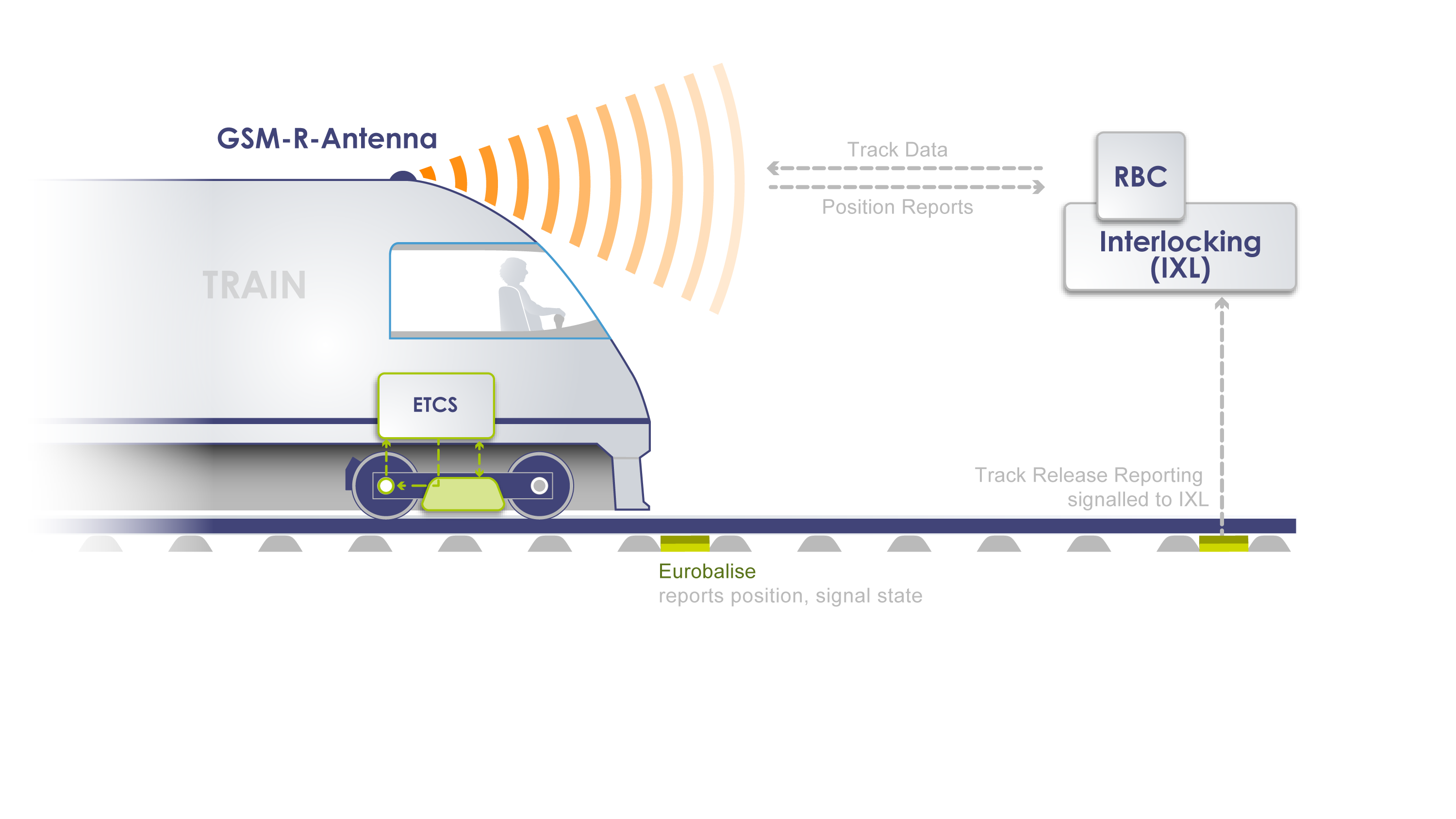

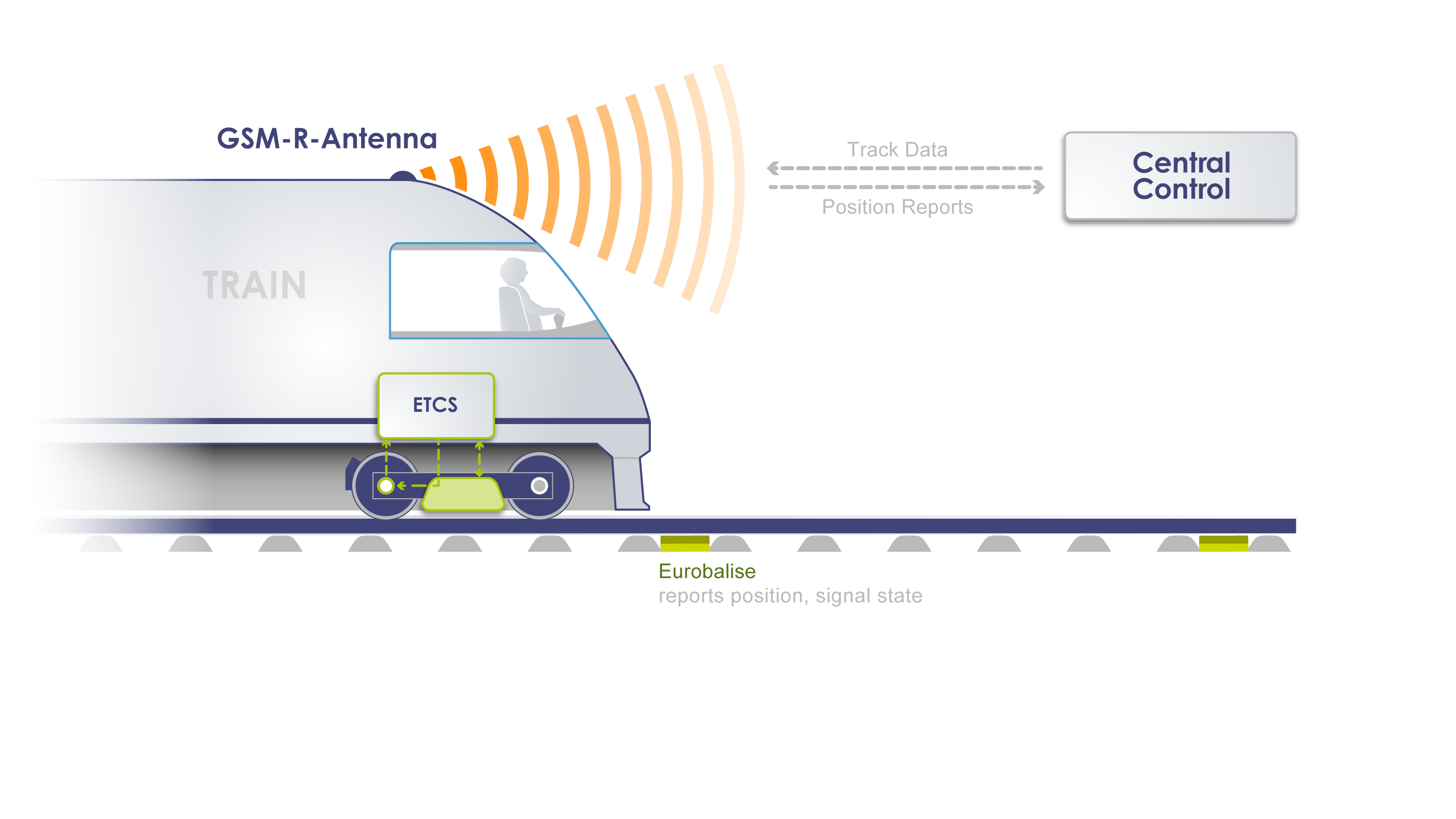

Despite these difficulties, there are also many benefits and opportunities for using a common track distance and a common train control system in Europe. For instance, it can facilitate cross-border travel and trade, reduce travel time and costs, enhance customer satisfaction and comfort, improve environmental performance and sustainability, and foster innovation and competitiveness in the rail sector. Therefore, it is important to continue to support and promote the implementation of the standard gauge and the ETCS in Europe, as they are essential for creating a single European railway area.


We share our key operational areas and the unique product that saves our clients’ budgets.


If you’re in logistics, you know the word “freight.” If you’re in Germany or Austria in February, you know the word “Fashing.” They sound similar. They share the same first letter. But the similarity ends there.


Container shipping is the backbone of modern international trade. Every day, millions of containers cross borders, delivering a vast variety of goods. However, there are clear rules defining what cannot be placed inside a container under any circumstances. Violating these prohibitions risks not only heavy fines and cargo confiscation, but also criminal liability, and in some cases, poses a real threat to life and the environment.


We say something else: “We’re already working on it.”


Amikor bérel vagy vásárol egy konténert, a megbízhatóságba és tartósságba fektet be. Gyakran feltett kérdés: “De hány évig fog így kibírni egy ilyen konténer?” Nézzük meg a tengeri konténerek élettartamát, és meséljünk arról, hogyan biztosítjuk Önnek a vállalatunk a legjobb kiindulást projektekhez.